Exercise is a very important part of a weight loss plan for a number of reasons.
Physical activity burns calories, which is essential for creating a calorie deficit necessary for weight loss. When you burn more calories than you consume, your body taps into stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss.
Regular exercise can increase your metabolism, which is the rate at which your body burns calories at rest. This means you’ll burn more calories throughout the day, even when you’re not exercising.
When you lose weight, you want to primarily lose fat rather than muscle mass. Exercise, particularly strength training, helps preserve lean muscle mass while promoting fat loss. This is important because muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue does, helping to support long-term weight maintenance.
Cardiovascular exercise, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, strengthens your heart and improves circulation. It also helps lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and decrease the risk of heart disease, which are important for overall health and well-being.
Exercise releases endorphins, which are neurotransmitters that boost mood and reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, increase energy levels, and enhance overall mental well-being, making it easier to stick to healthy eating habits and stay motivated to reach your weight loss goals.
Exercise not only burns calories during the activity itself but also increases energy expenditure afterward. This phenomenon, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) or the “afterburn” effect, means you continue to burn calories at an elevated rate for a period of time after your workout.
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining weight loss over the long term. It helps prevent weight regain by supporting a higher metabolic rate, preserving lean muscle mass, and promoting healthy habits that contribute to weight maintenance, such as increased physical activity levels and better dietary choices.
Overall, while diet plays a significant role in weight loss, exercise is equally important for achieving sustainable results, improving overall health, and enhancing quality of life. Combining a balanced diet with regular physical activity is the most effective approach for successful weight loss and long-term weight management.
Exercise preserves muscle as you lose fat.
When people lose weight without exercise they often lose muscle as well as fat.
This is a problem because muscle tissues burns more calories at res, losing muscle slows your metabolism and regaining weight (rebounding) become easier.
Resistance training signals to you body that you should keep muscle, It improves vody composition even if the number on you weight scales moves very slowly, and it makes your weight loss look a lot better, not just lighter.
Exercise Improves Metabolic Health
How exercise improves metabolic health is a really important factor to be informed on with weight-loss.

Insulin Sensitivity
A huge factor in this is how the body improves its insulin sensitivity. When you exercise, you muscles start pulling glucose out of your blood without you even needing that much insulin. In this case less insulin is needed to control blood sugar and the risk of type 2 diabetes is lowered
Metabolic Flexibility
Exercise enhances fat metabolism and metabolic flexibility. This trains your body to burn fat more efficiently and allows the body to switch between carbs and fat depending on availability. This ability is called metabolic flexibility which is often impaired in people who are obese or who have insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
Visceral Fat
Exercise reduces visceral fat. Visceral fat is the fat around organs that actively releases inflammatory chemicals that can ruin metabolism.
Exercise reduces visceral fat, it lowers inflammatory cytokines and improves liver function and insulin sensitivity. Even if the number on your weighing scales doesn’t change much losing visceral fat is really important for long term health as well as just weight loss.
Mitochondrial Function
The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell, it’s the part of the cell that provides energy to the cell.
Exercise increases the number of mitochondria and also makes the mitochondria of our cells work better. So as well as exercise increase the quantity, it increases the quality.
The mitochondria becomes more efficient at using oxygen and make them less likely to reduce electrons which create damaging free-radicals.
Exercise trains mitochondria to be able to switch fuels effectively; the body can burn fat at low/moderate intensities and burn carbohydrates at higher intensities.
It improves oxygen deliver throughout our bodies. The Mitochondria can’t work without oxygen. Exercise increases capillary densitiy around muscle fibre, blood flow efficiency and myoglobin content in muscle.
Healthy mitochondria improves the health of the entire body; they help with energy levels, fat loss, insulin sensitivity, and endurance and recovery.
Exercise doesn’t just burn calories; it reprograms how your body handles energy by influencing you metabolic health.
Regarding metabolic health people can improve blood sugar, lower insulin and reduce risk of disease.
Exercise Regulates Appetite & Hunger
Exercise regulate appetite and hunger hormones in a number of ways. Appetite isn’e just about “willpower” it is about hormone signalling and exercise can change that.
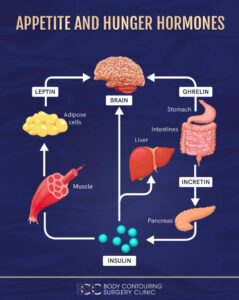
Ghrelin
Ghrelin is a hormone made in your stomach and it tells your brain to eat. Acute exercise (especially high-moderate intensity) can temporarily suppress ghrelin. This is why a lot of people feel less hungry after working out.
Over time exercise will regulate ghrelin production so hunger better matches energy needs.
Exercise doesn’t actually eliminate hunger it just normalizes it.
Leptin
Leptin is a hormone produced by your fat cells to tell your body that you’ve eaten enough.
A problem with a person’s metabolism may result in high leptin levels which after some time your body will stop reacting to, this called Leptin Resistance. This results in the individual feeling hungry even though there is plenty of stored energy.
Exercise will improve leptin sensitivity (Not just levels), it reduces inflammation in the hypothalamus (the key appetite control centre) and it lowers visceral fat which interferes with leptin signalling.
Peptide YY
Peptide YY (PYY) is the meal-ending hormone. It is released from the gut and it promotes fullness to let the individual know they’ve eaten enough.
Exercise will increase post-meal PYY, you will have stronger and longer-lasting satiety after eating and will reduce the urge to continue snacking.
This affect is especially strong after aerobic exercise.
Insulin – Not Just Your Blood Sugar, Your Appetite
Insulin can act in the brain as a satiety hormone. If the individual has insulin resistance the brain won’t “hear” the insulin’s “Stop Eating” signal and hunger may persist even with adequate calories.
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, it restores insulins appetite-suppressing effect and it reduces reactive hypoglycaemia that drives cravings.
Cortisol
Cortisol is the stress hormone. Chronic stress leads to elevated cortisol which in turn leads to cravings for sugar and fat.
Exercise can help by lowering baseline cortisol over time, it improves tress resilience and it enhances the normal cortisol rhythm (high morning, low evening)
Over-training or under-fuelling can increase cortisol, so it’s important to find a balance.
Short-Term & Long-Term
In the short-term, the hours after which you exercise, appetite generally drops, especially after HIIT, Running, cycling or heavy resistance training.
This is partly due to body temperature and blood flow shifts and stress horones like adrenaline.
In the long-term the appetite gets better regulated, not necessarily lower. Your body will learn to increase hunger when it’s really needed and decrease cravings when the energy balamce is already fine.
Good Exercises For Weight Loss
There are a number of specific exercises which are known as being the best for weight loss. The best exercises for weight loss are those which burn a lot of calories quickly, that are easy and safe to practice, and that will make your workout as efficient as possible.
Jump Rope is a great exercise because the only equipment you need is a jump-rope. If you jump at 120 skips per minute you will burn around 667-990 calories per hour.
You could even try using a weighted rope to give your arms a better workout. It is also really fun and it improves coordination.
Running is a basic but effective exercise. Running for just ten minutes, or just for a mile will go a long way to losing weight. Also, after a good run you will continue burning calories for the rest of the day.
You could invest in a treadmill. Because treadmills have been around for many years and can offer a great cardiovascular workout, not varying may quickly bore you and you may find yourself wanting a newer exercise machine. However, whether you are walking or jogging, the treadmill offers more calorie burning movements for the entire body than any other exercise machine. Many of the newer gadgets are not time-proven like the treadmill and may only work one area of your body. Whole body fitness is what you want for natural weight loss and toning.
Cardio exercises elevate your heart rate and helpburn calories effectively
Cycling Whether outdoors or on a stationary bike, cycling is a low impact cardio option.
Kickboxing is known to give a good full body workout that is effective for weight loss. You could join a kickboxing club. As well as being an effective workout you will be much more confident if you know how to effectively defend yourself.
A Rowing Machine will give a full cardiovascular workout. On a rowing machine you will have a full range of motion, working out your legs, arms and strengthening your core.
Yoga May not be as conventional, but works. You should sign up for a power vinyasa class or “Power yoga” this will also help you relax, your mind will be calmer and you’ll be more contented.
Interval Training incorporats high intensity intervals to you workout routine to boost calorie burning. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) uses alternating periods of short bursts of intense exercise followed by 10 seconds of rest.
Stength Traing;Building lean muscle mass can help increase your resting metabolic rate. you can out on muscle mass by weightlifting which incorporates using free weights, resistance bands or weight machines. You can also build muscle using bodyweight exercises.
Core workouts are important to build your overall strength and your stability.
In conclusion, exercise regulates appetite by suppressing hunger hormones short-term, increasing fullness hormones, improving brain appetite control, stabilizing blood sugar and reducing emotional and reward-based eating.
It doesn’t “kill hunger” it just makes it smarter and more effective.